Java | Serialization
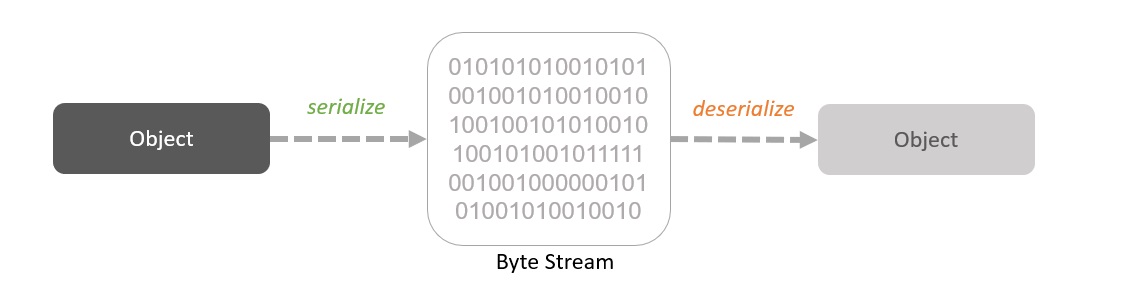
Serialization is the process of converting an object into a stream of bytes which can be deserialized back to a copy of the object. A serialized object can be stored in a file and deserialized later into an object.
Serializable Objects
- An object is serializable if it is a sub-type of
java.io.Serializableinterface or its sub-interfacejava.io.Externalizable. - Serializable objects can be stored into e.g. a file and restored back into an object by deserializing it.
- Serializable objects can be serialized using default Java way or custom way.
- Serializable object includes sufficient information to restore the fields in the stream to a compatible version of the class.
public class Universe implements Serializable {
private long timestamp;
public Universe() {
timestamp = System.currentTimeMillis();
}
}
Serializing an Object
ObjectOutputStream.writeObject(Object ob)method is used to write an object toOutputStreame.g.FileOutputStream.
public static void serialize(Universe universe) throws Exception {
FileOutputStream file = new FileOutputStream("output.txt");
ObjectOutputStream out = new ObjectOutputStream(file);
out.writeObject(universe);
out.close();
file.close();
}
Deserializing an Object
ObjectInputStream.readObject()method is used to read an object fromInputStreame.g.FileInputStream.
public static Universe deserialize() throws Exception {
FileInputStream file = new FileInputStream("output.txt");
ObjectInputStream in = new ObjectInputStream(file);
Universe universe = (Universe) in.readObject();
in.close();
file.close();
return universe;
}
Non-serializable Fields
- Fields declared as
transientorstaticwill not be serialized.
public class Universe implements Serializable {
public static Universe INSTANCE; //Non-serializable
private long timestamp;
private transient long age; // Non-serializable
public Universe() {
timestamp = System.currentTimeMillis();
}
}
Optional Methods for Serializable Class
- Classes implementing
Serializableinterface can optionally define the following methods:- writeObject() to control what is saved and append additional information to the stream.
- readObject() to update the state of the object after it has been restored.
- writeReplace() to replace object to be written to stream with different one.
- readResolve() to replace object read from stream with different object.