Algorithms for Finding all Possible Combinations of k Elements in an Array with Java Implementation
 Given an array of size N e.g.
Given an array of size N e.g. e={'A','B','C','D','E'} N=5, we want to find all possible combinations of k elements in that array. For example, if k=3 then one possible combination is {'A','B','C'}. Here we have three different algorithms for finding k-combinations of an array.
Forward-Backward Algorithm
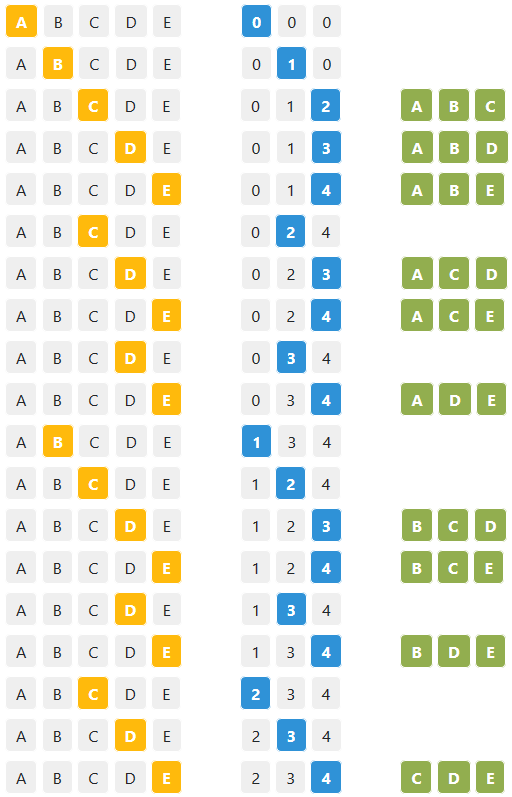
Here we have two arrays and two main indices r & i:
- Array e which is the elements array.
- Array pointers which is an array for holding indices for selected element.
- Index i for pointing to current selected element in array e.
- Index r for pointing to current position in pointers array.
- The algorithm will move forward by incrementing i & r as long as they do not exceed arrays length.
- If r reaches the last position of pointers array a combination is printed.
- If both indices reach the last poisition of their pointing arrays the algorith will step backward by reducing r value
r--and set i with the value ofi = pointer[r]+1.
public static void combination(Object[] elements, int k){
// get the length of the array
// e.g. for {'A','B','C','D'} => N = 4
int N = elements.length;
if(k > N){
System.out.println("Invalid input, K > N");
return;
}
// init combination index array
int pointers[] = new int[k];
int r = 0; // index for combination array
int i = 0; // index for elements array
while(r >= 0){
// forward step if i < (N + (r-K))
if(i <= (N + (r - k))){
pointers[r] = i;
// if combination array is full print and increment i;
if(r == k-1){
print(pointers, elements);
i++;
}
else{
// if combination is not full yet, select next element
i = pointers[r]+1;
r++;
}
}
// backward step
else{
r--;
if(r >= 0)
i = pointers[r]+1;
}
}
}
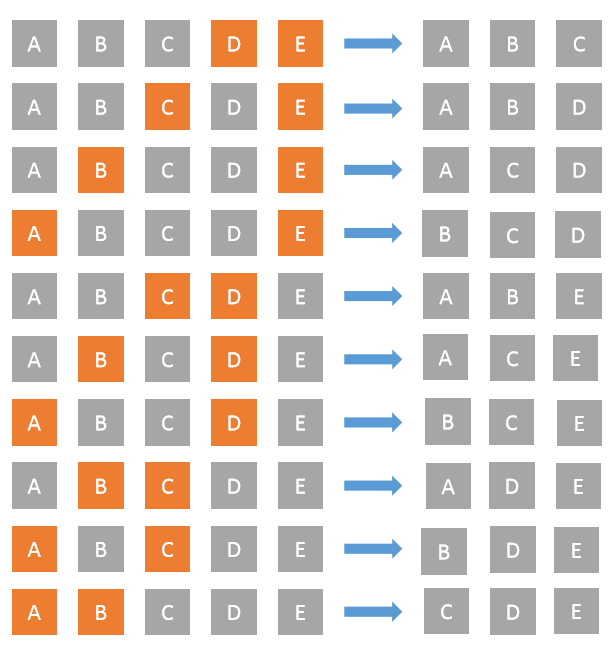
Shifting Algorithm
- This algorithm is more intuitive than the first one.
- We virtually split the elements array into two types of elements, k elements that can be selected and N-k elements that will be ignored.
- In each iteration we select N-k non-ignored elements.
- After each iteration we shift the positions of ignored elements as shown in the image below.
public static void combination(Object[] e, int k){
int[] ignore = new int[e.length-k]; // --> [0][0]
int[] combination = new int[k]; // --> [][][]
// set initial ignored elements
//(last k elements will be ignored)
for(int w = 0; w < ignore.length; w++)
ignore[w] = e.length - k +(w+1);
int i = 0, r = 0, g = 0;
boolean terminate = false;
while(!terminate){
// selecting N-k non-ignored elements
while(i < e.length && r < k){
if(i != ignore[g]){
combination[r] = i;
r++; i++;
}
else{
if(g != ignore.length-1)
g++;
i++;
}
}
print(combination, e);
i = 0; r = 0; g = 0;
terminate = true;
// shifting ignored indices
for(int w = 0 ; w < ignore.length; w++){
if(ignore[w] > w){
ignore[w]--;
if(w > 0)
ignore[w-1] = ignore[w]-1;
terminate = false;
break;
}
}
}
}
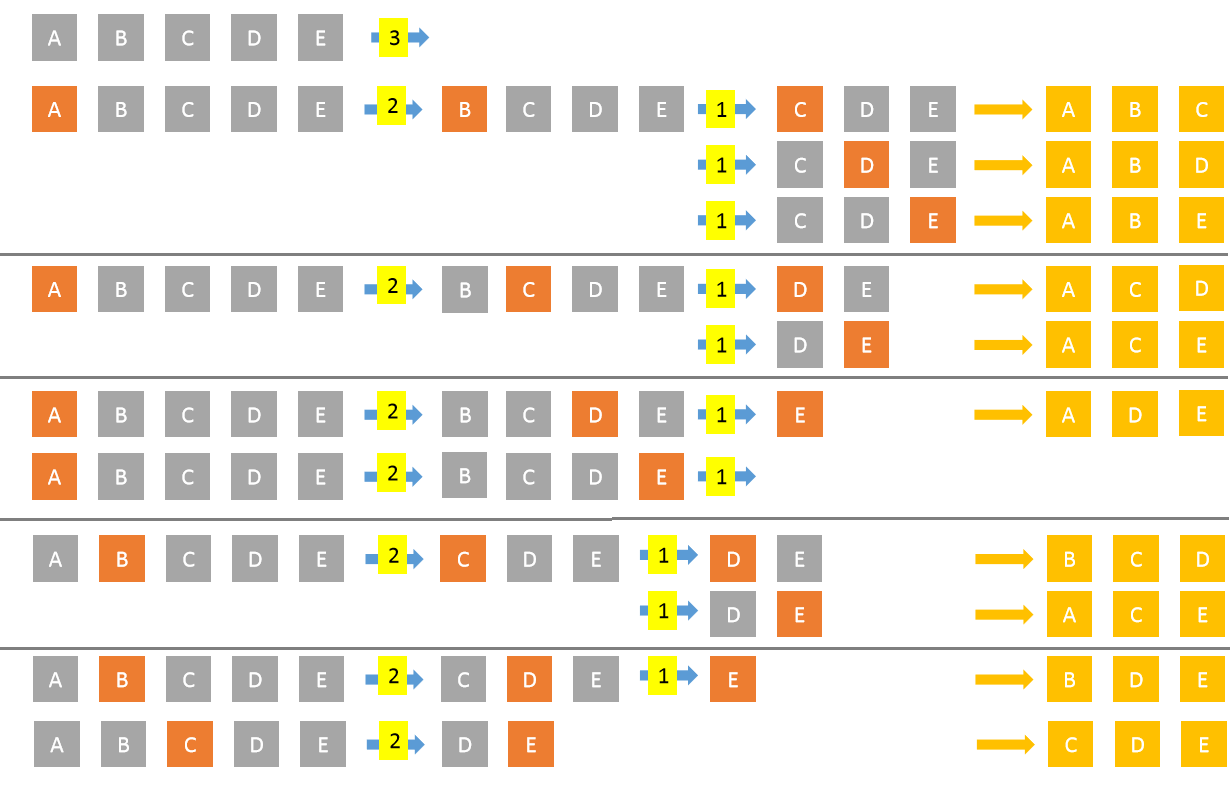
Recursive Algorithm
- Recursive algorithm has shorter steps.
- In each call to the function we pass List of elements, k and an accumulated combination.
- Then we have four conditions:
- if
elements.length < kthen stop - if
k == 1then add each element to the accumulated combination - if
elements.length == kthen add all elements to the accumulated combination. - if
elements.length > kthen for each elementemake a recursive call passing sub list of the elements list,k-1and add elementeto accumulated combination.
- if
- It works as shown below
public static void combination(List<String> e, int k, String accumulated){
// 1. stop
if(e.size() < k)
return;
// 2. add each element in e to accumulated
if(k == 1)
for(String s:e)
print(accumulated+s);
// 3. add all elements in e to accumulated
else if(e.size() == k){
for(String s:e)
accumulated+=s;
print(accumulated);
}
// 4. for each element, call combination
else if(e.size() > k)
for(int i = 0 ; i < e.size() ; i++)
combination(e.subList(i+1, e.size()), k-1, accumulated+e.get(i));
}